Revolutionizing Sustainable Agriculture with Bio-Gel®
Bio-Gel® technology is a carbohydrate-based hydrogel designed to enhance agricultural productivity by improving soil water and nutrient retention. This innovative solution addresses key challenges in modern farming, including water scarcity and nutrient management. Bio-Gel absorbs and retains water, gradually releasing it to crops, reducing irrigation needs and improving overall water-use efficiency. In addition to water retention, Bio-Gel enhances nutrient retention by trapping essential nutrients, preventing their leaching from the soil, and supporting soil organic matter formation. This, in turn, promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms, improving soil structure, fertility, and nutrient cycling for long-term soil health.
Sustainable, High-Performance Solution for Healthy Crops
Bio-Gel trials were conducted across various agricultural sites to assess its performance under different soil conditions and application methods. In-furrow applications were tested in Wisconsin, South Dakota, and North Dakota, representing a range of soil types common in these regions. Side-dress applications were implemented in Wisconsin, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, and Kansas. The trials spanned 27 soil types, ensuring a broad evaluation of Bio-Gel’s effectiveness in enhancing nutrient and water retention, soil health, and crop productivity across diverse farming environments.
Optimized Experimental Design for Effective Research and Data Analysis
Soil and plant tissue samples were collected from all sites according to Midwest Laboratories’ guidelines. Two soil analysis methods were employed: the ammonium acetate extraction (AAE) method and the saturated paste extraction (SPE) method. The AAE method reflects the long-term nutrient pool, while the SPE method represents short- to medium-term nutrient availability. By using both methods, we gained valuable insights into nutrient mobility and assimilation by plants.
Research Results: Key Findings and Insights for Bio-Gel on Corn
Nutrient Retention
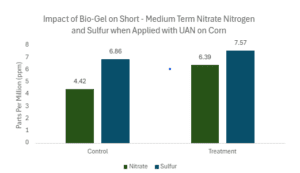
Bio-Gel significantly improved nutrient retention in corn. When applied as a side-dress with Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN), Bio-Gel increased short- to medium-term nitrate nitrogen availability by 44% across 11 soil types. At the Kansas site, the increase in nitrate nitrogen was even more pronounced, reaching 77%, which added approximately 23 pounds per acre to the top 8 inches of soil. Bio-Gel also increased sulfur retention by 35% when used in conjunction with in-furrow fertilizers, translating to a 15-pound per acre increase.
Soil Organic Carbon

Bio-Gel consistently increased soil organic carbon by 9% in corn trials, representing a 0.26% increase in overall soil organic carbon across six experimental sites. This result indicates a positive impact on soil health and structure.
The 2024 trials underscore Bio-Gel’s remarkable impact on crop productivity, particularly when applied in-furrow and as a side-dress with Urea Ammonium Nitrate (UAN) fertilizer. Bio-Gel significantly enhances nutrient retention and mobility in the soil, improving nitrate nitrogen availability by up to 44%, with a striking 77% increase observed at the Kansas site. Additionally, the in-furrow application of Bio-Gel increases sulfur retention by 35% and boosts soil organic carbon by 9%.
In Conclusion
These results highlight Bio-Gel’s potential to optimize fertilizer use efficiency and improve soil health, particularly in corn production systems. For farmers seeking to maximize both nutrient retention and crop yields, Bio-Gel’s application with UAN represents a strategic approach to enhance fertilizer effectiveness and support long-term soil sustainability. By incorporating Bio-Gel into your nutrient management plan, you can significantly improve crop performance while fostering healthier soils for future growing seasons.

